The Difference Between M2M and IoT – And Why It’s Important to Distinguish Between Them

Morten Riber | August 19, 2024

Many people use the terms M2M and IoT interchangeably, but did you know that there are significant differences between the two technologies that also make it important to distinguish between them?
In this blog post, we’ll give you a basic understanding of the differences, with a particular focus on how the terms are used in industry and business contexts.
What is M2M?
The M2M (Machine-to-Machine) technology connects machines, devices and appliances wirelessly via communication channels, including local area networks and SMS, to deliver services with limited human intervention. This connection upgrades the devices to intelligent assets, opening up a range of optimization opportunities
M2M technology is often used for automation and monitoring, where devices send data to either each other or a control center
Examples of M2M use cases:
- Automation in factories where machines control production processes without human intervention.
- Alarm and monitoring systems that automatically send data to control centers, for example when monitoring temperatures in refrigerators with expensive and sensitive contents.
- ATMs where the ATM sends transaction data to a central server, which then processes and validates the transaction.
What is IoT?
IoT (Internet of Things) refers to a wider network of physical devices connected to the internet. These devices, such as sensors and actuators, collect and share data via internet connections, providing a solid foundation for decision-making based on real-time data.
IoT is used in many different contexts, including:
- Smart home technologies for consumers: Devices like smart thermostats, washing machines and door locks.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): Optimizing production processes, monitoring equipment and improving safety in industrial environments.
- Energy management: Monitoring and optimizing energy consumption in buildings and factories.
- Optimizing supply: Water utilities save water using IoT technology by monitoring and optimizing water consumption in real time. This is made possible by using sensors to detect leaks and inefficient water use, which can then be quickly corrected.
- Optimizing agriculture: IoT devices are used in agriculture to improve food production. By implementing sensors that monitor soil moisture, temperature and nutrient levels, farmers can optimize their crop production.
Today, IoT is widely used in private households, but it is especially in business and industry that IoT can create great value and help optimize operations, productivity, maintenance and energy management.
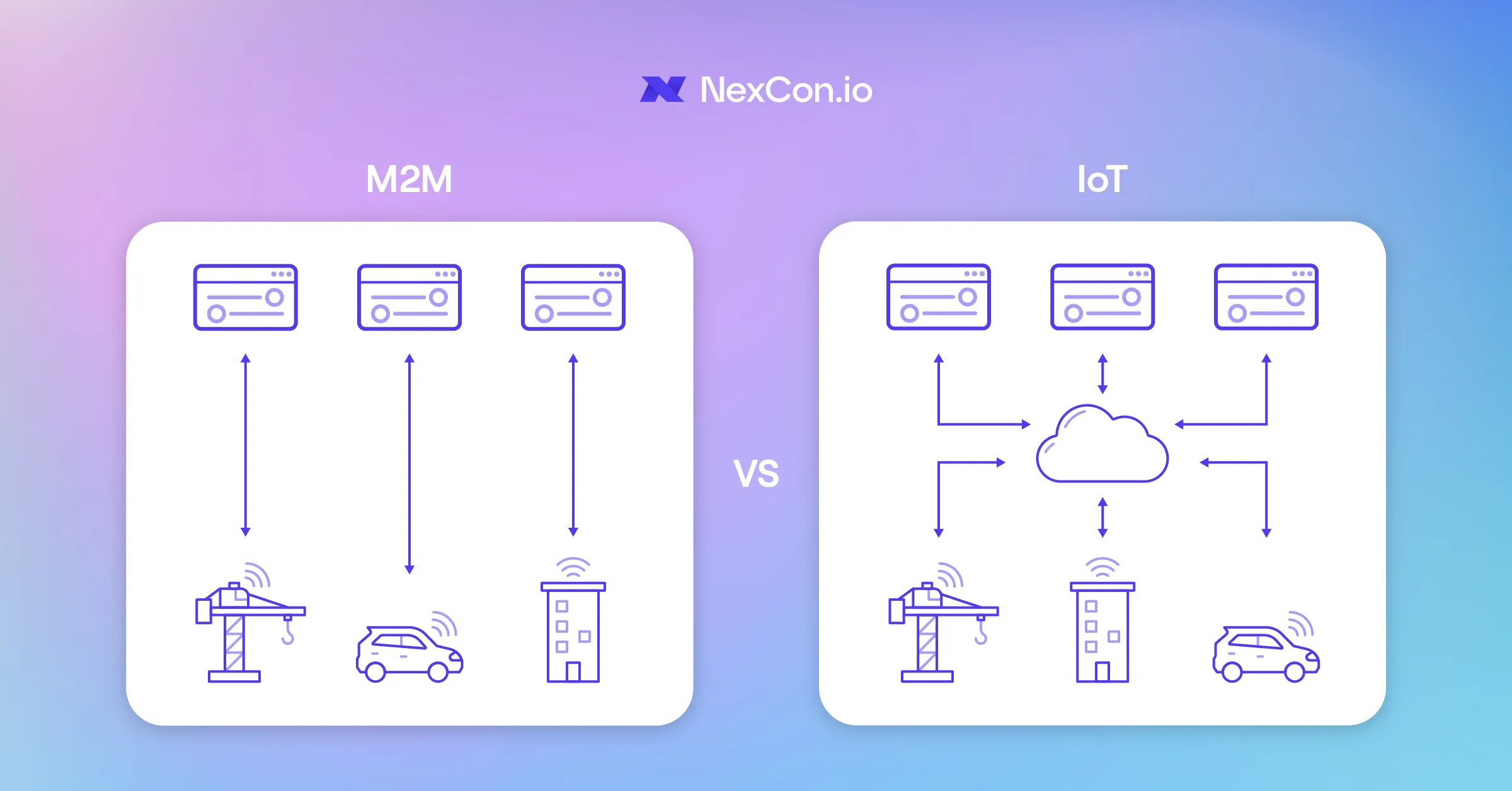
Significant differences between M2M and IoT
Although M2M and IoT share some common features, there are significant differences between them. We’ve outlined the most notable ones below:
Network
M2M does not necessarily require an internet connection and often uses local networks for data transfer, while IoT devices are connected to the internet and use cloud technology for data processing and storage.
Scalability
IoT systems are designed to be more flexible and easy to scale, making it easy to add new devices to the network. M2M often requires manual setup of each connection, which is more time consuming.
Interoperability
IoT offers greater interoperability by allowing connections between different devices and systems, which makes it more versatile for different applications. M2M systems often require specific programming for each device to communicate.
Data insights and human interaction
IoT systems provide greater data integration and enable users to analyze data and make decisions. M2M systems are more limited in their ability to deliver user-friendly data experiences.
Three fun facts about M2M and IoT
1) The number of IoT devices has surpassed the world population: In 2021, there were over 13 billion IoT devices in use and this number is expected to increase to 30.9 billion by 2025.
2) IoT generates large amounts of data: IoT devices are expected to generate over 79.4 zettabytes of data by 2025 (1 zettabyte = 1 billion terabytes).
3) IoT and M2M are key to Industry 4.0: Both technologies are central components of Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, where IoT and M2M help enable a more flexible, efficient and sustainable production process.
IoT SIM cards and M2M SIM cards
NexCon.io offers SIM cards designed for industrial use, supporting both M2M and IoT technologies.
We understand the importance of connectivity solutions that are both innovative and reliable. As a NexCon.io customer, you can buy IoT and M2M SIM cards directly in our webshop and easily manage them in the dashboard afterwards with several features available like data pools, mass editing and IMEI locking.
By choosing NexCon.io, you get unrivaled service, flexibility and quality to ensure your devices stay connected in an increasingly interconnected world.
Create a free account here or contact our sales team at hi@nexcon.io and we’ll work with you to find the best solution.
Conclusion
IoT and M2M are both crucial technologies in business and industry, but they serve different purposes. While M2M focuses on direct machine-to-machine communication without the internet, IoT extends this concept by connecting devices to the internet and creating a more comprehensive network of data and control. By using IoT SIM cards and M2M SIM cards, businesses can ensure reliable and efficient communication between their devices, enabling advanced applications and optimized operations.